Click the Props button  in the toolbar.
in the toolbar.
Double-click on a overlay object in the Map window.
Right-click an object and select Properties...
Your Marks, Routes, Tracks and Current Position are collectively known as Overlay Data.
The Overlay Properties window lets you display and edit the properties of various different kinds of overlay objects.
There are several ways you can open the Overlay Properties window:
Click the Props button  in the toolbar.
in the toolbar.
Double-click on a overlay object in the Map window.
Right-click an object and select Properties...

The left side of the Overlay Properties window shows the organization of overlays in different categories and sub-categories.
Use the check boxes to show or hide the overlays.
The right-click menu allows you to perform operations (such as Lock, or Delete) on all overlays in the category and sub-category.
To create a new sub-category, right click where you want it to appear, and click New Category in the pop-up menu. You can create nested sub-categories to any number of levels.
You can drag-and-drop items to move them to different categories.
When you Remove a sub-category, all it's contents are moved up to the parent category. You cannot remove a top-level category, but when you next open the Overlay Properties, the empty categories are removed.
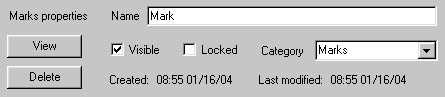
The following properties are common to all types of overlay:
Name: You can give your overlays a name, which can be as long as you like and can use punctuation or other special letters. The name is displayed in the tool-tip when you hover the mouse on the object.
View: Clicking this button opens the best available map, and scrolls and zooms it to show the object.
Visible: Clearing this checkbox removes the object from view. Use to un-clutter the display. Note, the visibility of Waypoints is controlled by the route(s) that they belong to. You cannot show or hide waypoints that are part of a route.
Locked: Checking this box prevents you from making changes to the object.
Delete: Permanently removes the object.
Created: The time and date the object was created.
Modified: The time and date the object was last modified or updated.

Total distance: The total length of the route. To change the distance units, use the Mode / Units menu.
Area: The enclosed area, shown only when the route is a closed loop (with the last waypoint being the same as the first one). If the route crosses over itself, the result may not be what you expect. The value calculated is the difference between the area enclosed to the left and the area enclosed to the right of the route.
Total ascent: The vertical height you have to climb along the route.
Total descent: The vertical height you descend along the route.
Est. Time: The estimated travel time. You specify the average speed by clicking the Settings button. The calculation also takes into account the amount of ascent and descent, by adding a time proportional to the height gain and loss.
Route card: Creates a "Route card" giving the summary and a table of the waypoints in the route. The Route Card is an HTML page, containing thumbnails of images linked to the waypoints, an overview map and elevation profile. You can print the information or copy it to another application.
Settings: Allows you to change the average speed and the coefficients for ascent and descent, used for calculating the estimated travel time. Also contains route card options. More info...
Label Legs: The course and distance on each leg is shown on the map. This information is also available in the pop-up tooltip, so this option is mainly useful when printing a hard copy.
Reverse: Change the direction of the route.
Waypoint list: The table shows the waypoints entered in the route, with positions, and the course and distance of each leg. Double-click a waypoint name to edit the waypoint properties.

Position: The coordinates of the mark/waypoint. You can edit the coordinates, following the same formatting as they are displayed.
Symbol: The graphic icon shown on the map at the position. You can define your own symbols using the Icons command in the Overlay menu.
Make default: When you enable this checkbox, the selected symbol becomes the default when you create new routes or waypoints.
Show name: If checked, the name is displayed on the map next to the mark. In the route elevation profile, this also causes the waypoint name and elevation to be shown. This is also used to mark "stage points" in a route card.
Alarm Radius: The distance from the mark, in meters for a proximity or anchor alarm. If Proximity is selected, the computer will beep once every time the GPS reports a position within the alarm radius. If Anchor is selected, the computer will beep when the GPS position is outside the alarm radius. The anchor alarm is only effective for a band 1 nautical mile outside the radius.
Name on GPS: A short name, usually only 6 characters, all uppercase with no spaces or punctuation. This is the waypoint's name displayed on the GPS. If you don't enter anything here, a name is automatically derived from the full name of the waypoint.
HotSpot file: The full path of the linked file. Use the Browse button to link a file to the Mark/Waypoint. When a file is linked, Right-click, Open will open the file with the associated application. If you want the file's desktop icon shown on the map, select "File icon" in the Symbol field. You can use this to link to digital photos, text notes, audio recordings, or any other application data. You can also create a HotSpot by dragging a file from Windows Explorer and dropping onto Memory-Map Navigator's map window.
Comment: A text area to record your comments attached to the mark or waypoint.
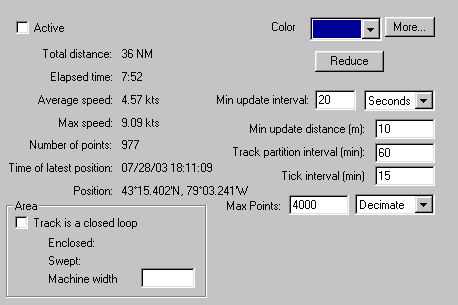
Active: New positions are added to the track only if this checkbox is set. If you want to terminate a tracklog and start a fresh one, clear this checkbox. If you want to resume an earlier track from the point where you left off, make it active. Only one track is active at any time.
Total distance: Total length of the track.
Elapsed time: Time difference from the start to the end of the track.
Average speed: Total distance divided by elapsed time.
Max speed: The maximum speed attained along the track.
Number of points: The number of points recorded.
Time of latest position: The time (from the GPS) of the last recorded position in the tracklog.
Position: The last recorded position.
Color: The color used to draw the track on the map. The More... button allows you to choose any color.
Reduce: Tracks are quite slow to draw, and if you have a long track, it may cause some flickering of the display each time the GPS records a position. Clicking this button removes every other recorded point in the track, making it faster to draw.
Min update interval: The minimum time interval between recorded track points. A new position from the GPS is recorded if this much time has passed since the last point recorded. If you want to disable recording a tracklog, set this to a large number of hours.
Min update distance: The minimum distance between recorded track points. A new position is only added if you have moved at least this distance since the last point.
Track partition interval: This value controls when to automatically start a new tracklog. When a new position is received from the GPS, if more than this time interval has passed since the last recorded position, and the distance from the last position is more than the Min update distance, then a fresh track is started. Eg, If you want to turn the computer on every six hours to check your position, and you want to record a track joining your positions, set the Track partition interval (in minutes) to a value more than six hours.
Tick interval: The ticks are the little arrows on the track, which are spaced at equal time intervals. Set the spacing between the arrows here. Set a value of zero to turn off the arrows.
Max Points: This is the maximum number of points that will be stored in the track. When the buffer is full, you can select Decimate (delete every other point) or Wrap (remove the oldest points).
Area enclosed: If the distance from the start point to the end point is less than 10% of the total length of the track, the enclosed area is calculated. Like the route area, if the track crosses over itself, the result may not be what you expect. The value calculated is the difference between the area enclosed to the left and the area enclosed to the right of the track.
Area swept: This is the total length of the track multiplied by the Machine width, expressed as an area. Enter the machine width in meters.
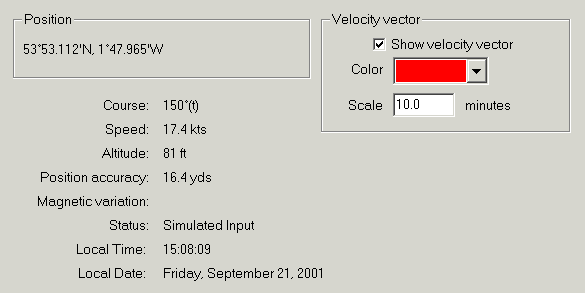
Position: The position last reported by the GPS. Use the Mode / Position format menu command to select different display units or grid coordinate systems.
Course: Your current direction of travel, as reported by the GPS. Use the Mode / Units / Magnetic variation menu command to display magnetic bearings.
Speed: Your current speed, as reported by the GPS. Use the Mode / Units menu to change the units.
Altitude: Your altitude as reported by the GPS (this may be above sea level, or it may be relative to the WGS84 spheroid).
Position accuracy: Estimated position error as reported by the GPS.
Magnetic variation: Some GPSs give an approximation to the magnetic variation at your current position. This is NOT used to set the magnetic variation for bearing display, as it is often not provided by the GPS.
Status: Description of the status of the GPS.
Local time, date: The time from the GPS, converted to local time using the computers localization settings.
Show Velocity Vector: Enables the arrow indicating your speed and direction of travel.
Color: Sets the color of the velocity vector. Note, this does not affect the color of the position icon, which is always red.
Scale: Controls the length of the velocity vector. The head of the arrow is placed where you would be after this period of time, if you were to maintain the same speed and course.

Position: The geographic coordinates of the top-left corner of the text box. You can edit the coordinates, following the same formatting as they are displayed.
Font: Use the windows font picker to select the appearance and size of the text.
Font color: Select the color of the text.
Background: Enable the Solid Background checkbox and click the Background button to select the background color.
Alignment: Select left, right or center text justification.
Multi-line: If this check-box is enabled, you can resize the text box by dragging it to the desired width. The height is automatically adjusted to fit the text.